Description
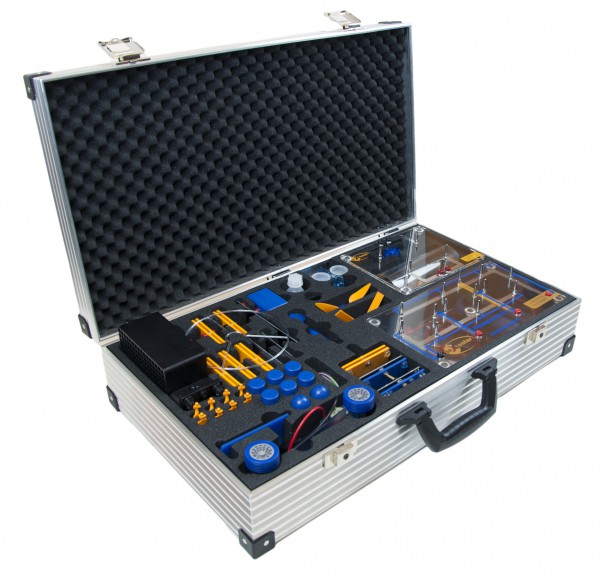
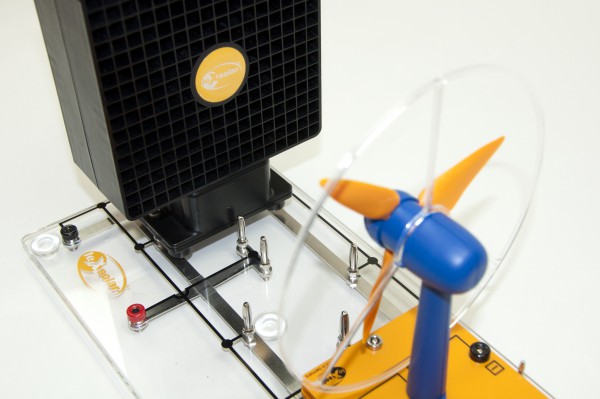
The leXsolar-NewEnergy Ready-to-go is specifically adapted for young students in Primary and Junior High School and provides by qualitative and quantitative experiments an understanding of the topics photovoltaic, wind power, hydro power, electric mobility and fuel cells. With the enclosed Smart Control components, an innovative measuring and control system is available and all necessary accessories like power supply, cables and measuring devices are already included.
Like the other products of the Ready-to-go line, the leXsolar-NewEnergy Ready-to-go amazes with its flexible and location-independent usability that doesn’t require any additional equipment.
Like the other products of the Ready-to-go line, the leXsolar-NewEnergy Ready-to-go amazes with its flexible and location-independent usability that doesn’t require any additional equipment.
Components
1x 1100-02 Solar module 0.5 V, 840 mA
1x 1100-07 Solar module 1.5 V, 280 mA
1x 1100-19 leXsolar-Base unit Large
1x 1100-20 Lighting module
1x 1100-23 Potentiometer module
1x 1100-25 Buzzer module
1x 1100-26 Light bulb module
1x 1100-27 Motor module without gear
1x 1100-28 Color discs - Set 1
1x 1100-29 Solar cell cover set (4 pieces)
1x 1100-31 Solar module 2.5 V, 420 mA
1x 1600-02 Capacitor module 5.0F/5.4V
1x 1400-08 LED-module 2mA, red
1x 1400-12 leXsolar-Wind rotor set
1x 1400-19 Wind machine
1x 1400-21 Wind rotor set (assemblied)
1x 1400-22 Wind turbine module
1x 1602-01 leXsolar-Base unit small
1x 1602-02 Hand generator
1x 1800-15 Distilled water (100 ml)
1x 1801-02 Electric model car
1x 1900-01 Water wheel module
1x 9100-03 AV-Module
1x 9100-05 PowerModule
1x L2-02-051 Silicone tube 12 mm
1x L2-06-012 Test lead black 25 cm
1x L2-06-013 Test lead red 25 cm
2x L2-06-014 Test lead black 50 cm
1x L2-06-015 Test lead red 50 cm
2x L2-06-033 Short-circuit plug
1x L2-06-067 Reversible Fuel cell
1x L3-01-175 Insert NewEnergy Rtg 2003
1x L3-03-220 Instruction for use of finger protector
1x L3-01-187 Case NewEnergy RtG 2003
1x L3-03-258 Info sheet initial startup
1x L3-03-259 Layout diagram 2003 leXsolar-NewEnergy RtG
1x L3-01-200 Deckelschaum mit Noppen
1x 1100-07 Solar module 1.5 V, 280 mA
1x 1100-19 leXsolar-Base unit Large
1x 1100-20 Lighting module
1x 1100-23 Potentiometer module
1x 1100-25 Buzzer module
1x 1100-26 Light bulb module
1x 1100-27 Motor module without gear
1x 1100-28 Color discs - Set 1
1x 1100-29 Solar cell cover set (4 pieces)
1x 1100-31 Solar module 2.5 V, 420 mA
1x 1600-02 Capacitor module 5.0F/5.4V
1x 1400-08 LED-module 2mA, red
1x 1400-12 leXsolar-Wind rotor set
1x 1400-19 Wind machine
1x 1400-21 Wind rotor set (assemblied)
1x 1400-22 Wind turbine module
1x 1602-01 leXsolar-Base unit small
1x 1602-02 Hand generator
1x 1800-15 Distilled water (100 ml)
1x 1801-02 Electric model car
1x 1900-01 Water wheel module
1x 9100-03 AV-Module
1x 9100-05 PowerModule
1x L2-02-051 Silicone tube 12 mm
1x L2-06-012 Test lead black 25 cm
1x L2-06-013 Test lead red 25 cm
2x L2-06-014 Test lead black 50 cm
1x L2-06-015 Test lead red 50 cm
2x L2-06-033 Short-circuit plug
1x L2-06-067 Reversible Fuel cell
1x L3-01-175 Insert NewEnergy Rtg 2003
1x L3-03-220 Instruction for use of finger protector
1x L3-01-187 Case NewEnergy RtG 2003
1x L3-03-258 Info sheet initial startup
1x L3-03-259 Layout diagram 2003 leXsolar-NewEnergy RtG
1x L3-01-200 Deckelschaum mit Noppen
Experiments
Experiments Primary level
1. From muscular strength to current...to light
2. From muscular strength to current...to motion
3. From muscular strength to current...to Noise
4. The solar cell drives a motor
5. The solar module powers a buzzer
6. The solar module powers a LED
7. The larger the solar cell, the ...?
8. The solar module powers a LED
9. From the solar cell to the solar module
10. Shading of solar modules
11. The wind turbine powers a buzzer
12. The wind turbine powers a LED
13. Influence of the wind direction
14. Influence of the rotor blade shape
15. Influence of the wind speed
16. The water wheel powers a buzzer
17. Influence of the water falling height
18. Storage of solar energy
19. Storage of wind energy
20. What is an Elektrolyzer?
21. How can water be split?
22. What is a fuel cell?
23. The fuel cell drives the motor
24. The fuel cell powers the buzzer
25. Energy demand of several consumers
26. Comparison of light bulb and LED
27. Storage and output of energy...EMobility
Experiments Secondary level
1. Forms of energy and consumers
2.1. Basic structure: rotation discs
2.2 Color qualities
2.3 Mixing colors
2.4 Color-deception with the Benham-disk
2.5 Relief-disk
3. Dependence of power of a solar cell on its area
4.1 Dependence of solar cell power on angle of incidence of light (qualitative)
4.2 Dependence of solar cell power on angle of incidence of light (quantitative)
5. Dependence of power of a solar cell on the illumination intensity
6.1 Dependence of solar cell power on load
6.2 The I-V-characteristics and filling factor of a solar cell
6.3 Dependence of I-V-characteristics of a solar cell on illuminance
7.1 Influence of changing wind speeds (qualitative)
7.2 Influence of wind speed on the wind turbine (quantitative)
8. Start-up wind speed at a wind turbine
9. Changing the turbine voltage by connecting several consumers
10. Characteristic curves of a wind turbine
11.1 Influence of the number of rotor blades (qualitative)
11.2 Influence of the number of rotor blades (quantitative)
12.1 Influence of the wind direction (qualitative)
12.2 Influence of the wind direction (quantitative)
13.1 Influence of the rotor blade pitch (qualitative)
13.2 Influence of the rotor blade pitch (quantitative)
14.1 Influence of the blade shape (qualitative)
14.2 Influence of the rotor blade shape (quantitative)
15.1 Water as an energy source (qualitative)
15.2 Water as an energy source (quantitative)
16.1 Influence of the water falling height (qualitative)
16.2 Influence of the water falling height (quantitative)
17. What does an electrolyzer?
18. What does a fuel cell?
19. Characteristic curve of the electrolyzer
20. Characteristic curve of the fuel cell
21. Operation of the electric car with the reversible fuel cell
1. From muscular strength to current...to light
2. From muscular strength to current...to motion
3. From muscular strength to current...to Noise
4. The solar cell drives a motor
5. The solar module powers a buzzer
6. The solar module powers a LED
7. The larger the solar cell, the ...?
8. The solar module powers a LED
9. From the solar cell to the solar module
10. Shading of solar modules
11. The wind turbine powers a buzzer
12. The wind turbine powers a LED
13. Influence of the wind direction
14. Influence of the rotor blade shape
15. Influence of the wind speed
16. The water wheel powers a buzzer
17. Influence of the water falling height
18. Storage of solar energy
19. Storage of wind energy
20. What is an Elektrolyzer?
21. How can water be split?
22. What is a fuel cell?
23. The fuel cell drives the motor
24. The fuel cell powers the buzzer
25. Energy demand of several consumers
26. Comparison of light bulb and LED
27. Storage and output of energy...EMobility
Experiments Secondary level
1. Forms of energy and consumers
2.1. Basic structure: rotation discs
2.2 Color qualities
2.3 Mixing colors
2.4 Color-deception with the Benham-disk
2.5 Relief-disk
3. Dependence of power of a solar cell on its area
4.1 Dependence of solar cell power on angle of incidence of light (qualitative)
4.2 Dependence of solar cell power on angle of incidence of light (quantitative)
5. Dependence of power of a solar cell on the illumination intensity
6.1 Dependence of solar cell power on load
6.2 The I-V-characteristics and filling factor of a solar cell
6.3 Dependence of I-V-characteristics of a solar cell on illuminance
7.1 Influence of changing wind speeds (qualitative)
7.2 Influence of wind speed on the wind turbine (quantitative)
8. Start-up wind speed at a wind turbine
9. Changing the turbine voltage by connecting several consumers
10. Characteristic curves of a wind turbine
11.1 Influence of the number of rotor blades (qualitative)
11.2 Influence of the number of rotor blades (quantitative)
12.1 Influence of the wind direction (qualitative)
12.2 Influence of the wind direction (quantitative)
13.1 Influence of the rotor blade pitch (qualitative)
13.2 Influence of the rotor blade pitch (quantitative)
14.1 Influence of the blade shape (qualitative)
14.2 Influence of the rotor blade shape (quantitative)
15.1 Water as an energy source (qualitative)
15.2 Water as an energy source (quantitative)
16.1 Influence of the water falling height (qualitative)
16.2 Influence of the water falling height (quantitative)
17. What does an electrolyzer?
18. What does a fuel cell?
19. Characteristic curve of the electrolyzer
20. Characteristic curve of the fuel cell
21. Operation of the electric car with the reversible fuel cell
Assembly Plan
Product Video
Sales are exclusively for entrepreneurs, business owners, freelancers, and public institutions. Please also refer to our terms and conditions as well as privacy policy.